Reverse Osmosis (RO)
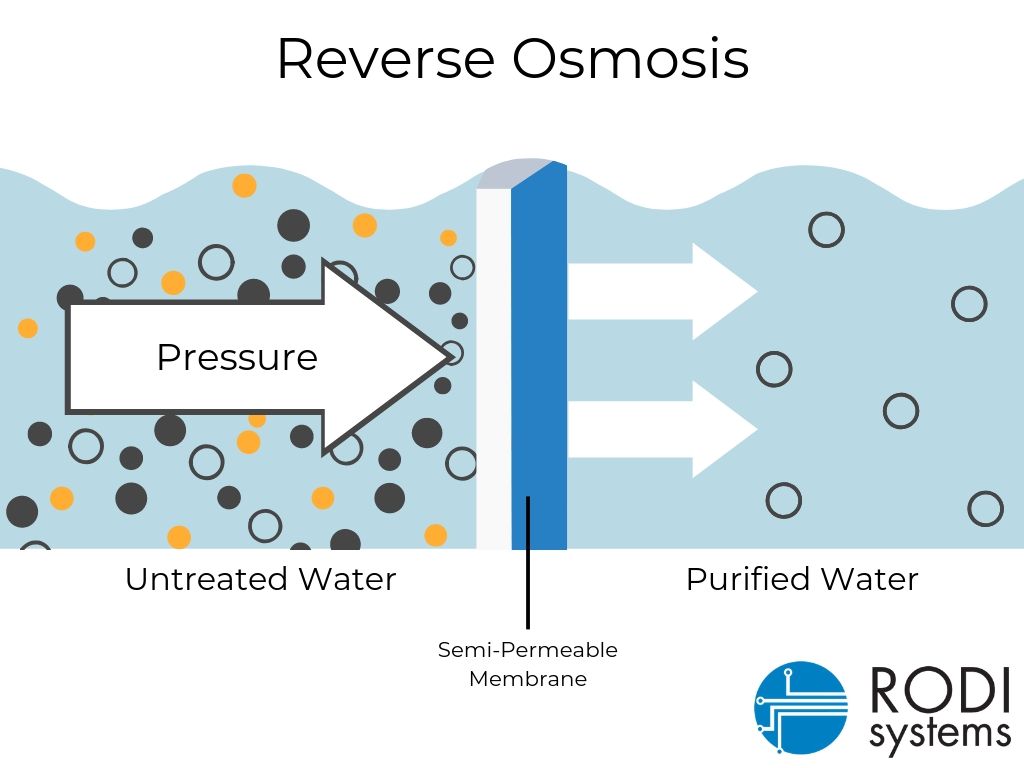
- Purpose: RO is a water purification process that removes contaminants from water by forcing it through a semi-permeable membrane.
- How it Works: The membrane allows water molecules to pass through but blocks larger molecules like salts, bacteria, and other impurities. It’s commonly used in desalination and in industries where high-purity water is required.
- Applications: RO is widely used in households for drinking water purification, in industries, and in wastewater treatment.
Ultraviolet (UV)
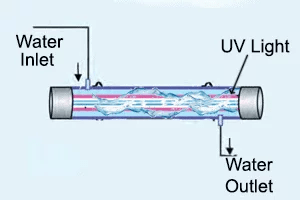
- Purpose: UV treatment is used to disinfect water by killing or inactivating harmful microorganisms like bacteria, viruses, and protozoa.
- How it Works: Water is exposed to UV light, which penetrates the cells of microorganisms and disrupts their DNA, rendering them incapable of reproducing and causing harm.
- Applications: UV is used in conjunction with other filtration systems to provide an additional layer of protection, often in drinking water systems and aquariums.
Sewage Treatment Plant (STP)

- Purpose: An STP treats domestic sewage to remove contaminants and produce environmentally safe treated wastewater (or effluent).
- How it Works: The process typically involves several stages: primary treatment (physical separation of solids), secondary treatment (biological treatment to break down organic matter), and tertiary treatment (advanced processes like filtration and disinfection).
- Applications: STPs are used in residential complexes, industries, and municipalities to treat wastewater before discharging it into the environment or reusing it.
Effluent Treatment Plant (ETP)
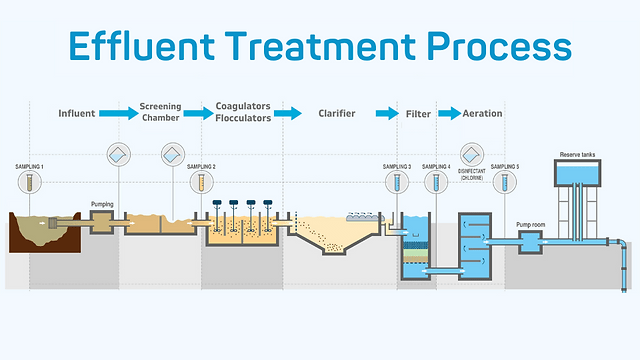
- Purpose: ETPs are designed to treat industrial wastewater by removing toxic substances and making the water safe for reuse or discharge.
- How it Works: The treatment process varies depending on the type of industry but generally includes physical, chemical, and biological processes to remove contaminants.
- Applications: Commonly used in industries such as textiles, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, and food processing.
Zero Liquid Discharge (ZLD)
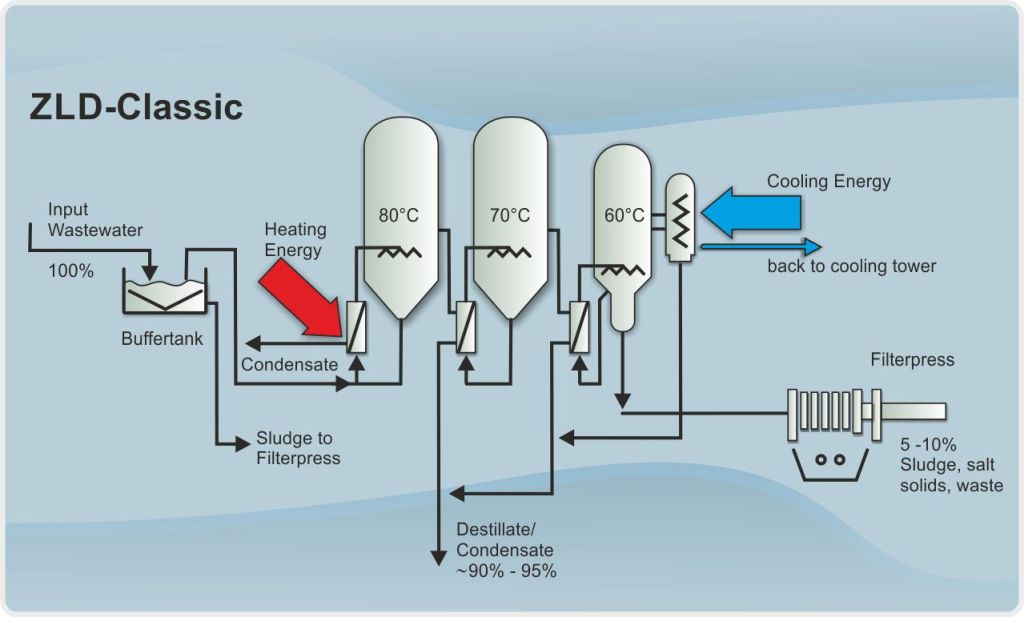
- Purpose: ZLD is a water treatment process that aims to eliminate all liquid waste from a system, leaving only solid waste for disposal.
- How it Works: The process involves multiple stages, including RO, evaporation, and crystallization, to recover water and minimize waste. The recovered water is typically reused within the process, reducing water consumption.
- Applications: ZLD is used in industries where wastewater discharge is highly regulated, such as power plants, petrochemical industries, and manufacturing facilities.
